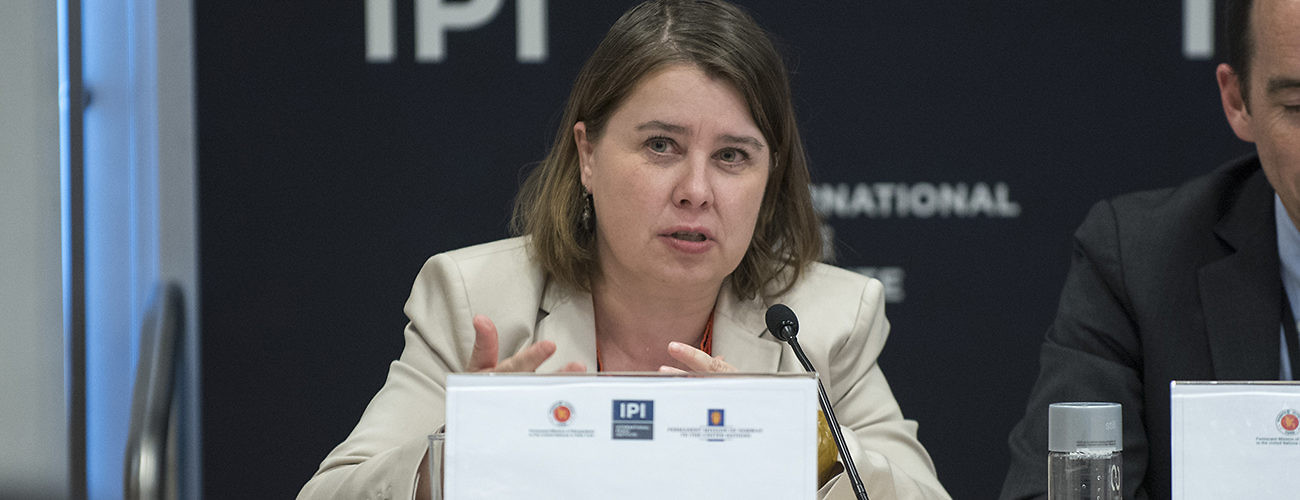
IPI Senior Visiting Fellow Alexandra Novosseloff told an IPI policy forum that aviation assets, the United Nations’ second biggest expenditure after personnel, were chronically shortchanged in mission planning, making them the “Achilles heel” of UN peacekeeping. “Ultimately it’s not UN rules that are the problem, it’s the persistent lack of needed assets and capabilities combined with the reluctance to use them that causes problems,” said Dr. Novosseloff, author of an IPI report on how UN missions’ air assets are organized, generated, managed, tasked, controlled, and commanded.
“As these expensive assets are scarce, relative to the large size of the territories covered, and often lack all the required capabilities, there is a chronic shortage of military air assets and, in particular, helicopters, in peacekeeping operations,” she said. “The financial pressure has already led some missions to further ‘rationalize’–meaning ‘reduce’–the use of their air assets, and the effect is that missions are less mobile and more constrained.”
She spoke at a May 1st IPI policy forum to launch the report, co-sponsored by the Permanent Missions of Bangladesh and Norway to the UN. Tareq Md. Ariful Islam, Bangladesh’s Deputy Permanent Representative, opened the meeting by noting the importance of aviation in gathering peacekeeping intelligence, protecting civilians, and assuring the security of peacekeepers. But, he added, “The deployment of air assets is fraught with a number of challenges, both practical and procedural.”
May-Elin Stener, the Deputy Permanent Representative of Norway, singled out three specific problems. She said that the Secretariat should play a greater role in matchmaking for multinational rotation contributions, that cost-saving decisions to travel over land rather than by air should be reconsidered, given the increasing number of attacks on patrols and logistical convoys, and that air threat assessments by UN missions ought to be strengthened and better aligned with the judgments of the troop-contributing countries (TCCs).
One reform Dr. Novosseloff suggested was using national or regional aviation capacity for logistical tasks through partnerships with national companies in addition to subcontracting to international companies who have less local knowledge. Arguing for a more efficient approach to making the assets more applicable to the task at hand, she cited a negative example. “Why equip helicopters with night vision when they are not allowed to fly at night by the host nation?” she asked. “Requirements should be more realistic regarding the capacities of contributing countries.”
Air Commodore Muhammad Mafidur Rahman of the Bangladesh Air Force suggested that troop contributing countries be included in the original preparation and drafting of mandates to improve operational coordination so that there is a “realistic” assessment beforehand of their ability to contribute assets. This would set a “more congenial” atmosphere and create needed “mutual trust and respect,” he said.
Gregory Pece, chief of the Air Transport Section, Logistics Support Division of the UN Department of Field Support (DFS), related that his challenge in enhancing the cost effectiveness and efficiency of UN aviation was not about “doing more with less or the same with less but doing less with less—this is the financial environment in which we live.”
He enumerated a series of cost saving measures to meet military requirements, determine the capabilities of aircraft, crew and equipment, and track the movement of people and cargo. Getting them approved and installed would depend in part on getting the most reliable data possible, he said. “We need to come up with consistent, presentable, clear modes of presenting data so we can look at utilization.”
Jorge Jackson, chief of air operations at the UN Mission in South Sudan (UNMISS), said air operations in Africa had improved in the five years he has been with UNMISS but that improvisation was always necessary given the state of infrastructure on the continent. “Aviation is an interesting tool, but aviation is not the problem solver,” he said. “We have to realize that what we see here from the headquarters, when you go to the ground, it is something else.”
Patrick Cammaert, a retired Dutch Major General with command experience in UN peacekeeping missions in Africa and Eastern Europe, told of past experiences where UN missions lacked the means to do the assigned job. “We all know that criteria for success for a peacekeeping mission is an achievable mandate and the resources to match,” he said.
IPI Vice President Adam Lupel moderated the discussion and in a concluding comment acknowledged that air assets for UN operations are too often “taken for granted. But,” he said, “if you dig a little bit below the surface–or above the surface as the case may be–you see that this is a topic with broad consequences, not just for UN peacekeeping, but for UN strategic effectiveness at large.”