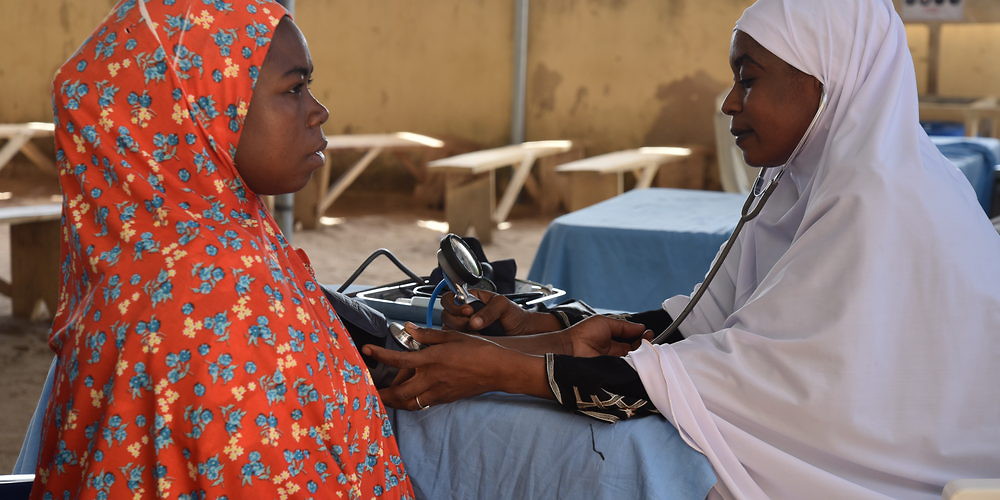
Aishatou, a midwife, provides an antenatal consultation for Fatima, who is seven months pregnant. Maiduguri, Nigeria, May 18, 2017. Jean Christophe Nougaret/MSF.
Armed conflict is a global health issue. Long-lasting and protracted conflicts in particular have consequences not only for the war-wounded but also for the health of entire communities. Over the years, global health actors and humanitarian health actors have developed health policies, guidelines, frameworks, and structures to improve delivery of health services in emergencies or humanitarian crises. Despite these advancements, however, the international health response in conflict-affected settings still faces gaps and challenges. Some policies and frameworks need to be rethought or redesigned, while others need to be better implemented.
This paper explores challenges to healthcare provision in conflict-affected settings. These challenges are broadly broken down into three categories: constraints related to the health system and damaged health infrastructure, difficulty for health workers to access populations in need, and restrictions to healthcare provision intentionally or accidentally placed by donors or states engaged on humanitarian and health issues (e.g., through the securitization of healthcare).
Tackling these challenges will have a direct impact on the lives of people in conflict-affected settings. However, doing so requires a radical shift in mindsets and the incentives that guide the actions of international health actors. Even so, more incremental changes can also be beneficial. To that end, this report puts forth the following recommendations:
- Improve coordination between and among humanitarian, development, and global health actors;
- Respond to context-specific needs;
- Hold health actors accountable to affected populations for their performance, and;
- Make responses sustainable.
This work is based on a combination of desk research, interviews with more than seventy key informants, and an expert meeting bringing together key stakeholders and experts on global and humanitarian health.