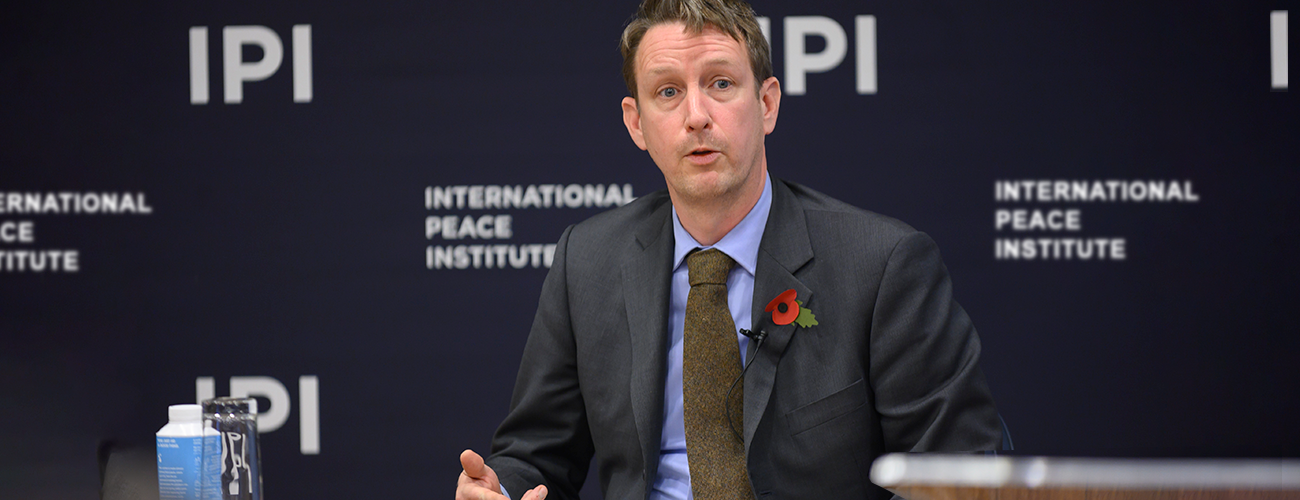
Just weeks after the committee named Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed as the 2019 laureate IPI hosted Asle Toje, a member of the Norwegian Nobel Committee, for a conversation about the prize.
Introducing Dr. Toje at the November 6th event, IPI Vice President Adam Lupel recalled that when he spoke at IPI for the first time last year, he said that “it is no exaggeration to say that the Nobel Peace Prize is the most prestigious prize in the world.” Mr. Lupel remarked, “It must also be added that to be on the committee is itself quite a prestigious honor.” Dr. Toje is the youngest member of the five person Norwegian Nobel Committee, which is chosen by the Norwegian parliament.
Dr. Toje began his remarks with a brief background of Alfred Nobel’s life and how he earned the considerable fortune that led him to write what Dr. Toje called “one of the world’s most famous wills and testaments,” therein instituting prizes in physics, physiology, chemistry, literature, and peace.
According to Dr. Nobel’s will, which both Dr. Lupel and Dr. Toje cited in their discussion, the prize for peace is to be awarded to “the person who shall have done the most or the best work for fraternity between the nations and the abolition or reduction of standing armies and the formation and spreading of peace congresses.”
Dr. Toje explained that since the first Nobel Peace Prize was awarded in 1901, there has been an ongoing debate about how to interpret the relatively brief and broadly general language in the criteria for the peace prize. While Alfred Nobel could not have conceived of the relevance of climate change or human rights in his lifetime, Dr. Toje explained that the Nobel Committee has adopted a “dynamic interpretation” to account for the importance of modern day issues.
The committee’s interpretation and application of Dr. Nobel’s will and testament is evident in the way that the selection of laureates has reflected contemporary priorities over the past century. Dr. Toje pointed out that after the first World War, the selection of winners centered around the League of Nations. Then, after World War II, “no issue was given more focus than nuclear disarmament.” More recently, the committee has focused on such issues as women’s rights, human rights, and climate change.
Regarding those who claim to have been nominated for the prize, Dr. Toje said that while the committee “will not speak against” such claims, the list of nominees remains confidential for 50 years, and the committee is bound to secrecy until lists are released. Still, he explained that every year, the committee receives questions from people claiming to have been nominated, asking if there is a diploma or a consolation prize. “Sadly,” Dr. Toje explained, “ we don’t we don’t give any runner-up medals.”
When asked about the relevance and diversity of the prize winners, Dr. Toje explained that the committee tries not to judge “different actors by different standards.” He elaborated, saying, “There is a tendency, at least in Europe, to be a bit cavalier about developments in Africa.” To Dr. Toje, this indicates that “we need to check development in Africa and in the Middle East,” where many of the world’s conflicts exist, and “if that means that we just have to really read up on the politics and the religious affairs of countries that we know little about before we start the process, so be it.”
Dr. Toje also addressed the relevance of international institutions in the future of promoting peace, admitting, “We’re facing a global challenge unlike anything we have seen in the past.” He believes that there is still a great deal of work to be done, and stated “I do believe that the United Nations will have a core role to play in this.” Though power balances and dynamics are shifting around the world, Dr. Toje pointed out that the UN has successfully overcome such challenges in the past and will continue to do so in the future. “I do believe that international institutions and multilateral cooperation is the path forward.”
Though much of the discussion focused on the history of the prize, Dr. Lupel asked Dr. Toje to place himself in the future, posing the question “When you look back on the Nobel Peace Prizes of this period, what do you hope to see?” Dr. Toje said he would hope that the Nobel Committee continues to “take its job seriously.” He continued, “We have this opportunity, once a year, to shine the light of global attention at one single issue, so we must choose carefully.”
In answering questions about the impact of the prize, Dr. Toje said the Nobel Peace Prize is always controversial. “There are always some people who feel that this laureate was the wrong one,” he admitted, highlighting that when Kailash Satyarthi was named a laureate in 2014, his award was not well-received within his own Brahmin community. Sharing further examples of controversial laureates, Dr. Toje remarked that Barack Obama’s award remains “deeply controversial,” and that while the selections of Nelson Mandela and Mother Teresa received criticism at the time, they are looked back on as “among sort of the stellar moments of the Nobel Peace Prize.”
However, Dr. Toje added, “Once the announcement has been made, we realize it lives its own life,” alluding to the intensity of public reactions. “If the Nobel Peace Prize didn’t spark outrage and strong emotions, well, we wouldn’t be living up to our reputation.”