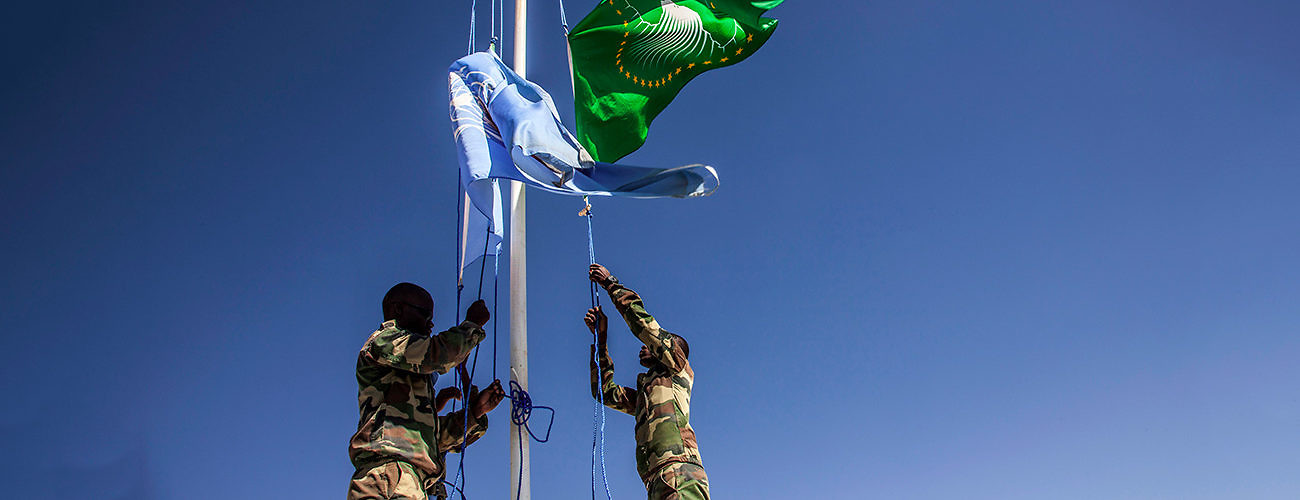
UNAMID officially hands over its team site in Tine, North Darfur, to the government of Sudan, October 19, 2017. Mohamad Almahady/UNAMID.
In the face of evolving security dynamics and geopolitical pressures, the African Union (AU) Peace and Security Council and the UN Security Council initiated the withdrawal of the AU-UN Mission in Darfur (UNAMID) in 2017. This transition is a uniquely complex undertaking—all the more so following Sudan’s political revolution in April 2019, which required the UN and AU to rapidly adapt their support to the country. This complex environment is putting all the principles of peacekeeping transitions to the test.
This paper examines the dynamics of this peacekeeping transition in Darfur, focusing on UNAMID’s drawdown and reconfiguration, as well as the UN’s efforts to build the capacity of other actors to sustain peace following the mission’s exit. It highlights five broad priorities for this transition going forward:
- Strengthening political engagement between the UN Security Council and AU Peace and Security Council;
- Translating the AU-UN joint political strategy into an effective follow-on presence;
- Reinforcing the transition concept;
- Integrating human rights and protection in all areas of work; and
- Sustaining international attention and financial support.
This paper is part of a larger IPI project on UN transitions and is complemented by similar case studies on UN peacekeeping transitions in Côte d’Ivoire, Haiti, and Liberia, as well as a paper exploring experiences and lessons from these three transitions.