Author
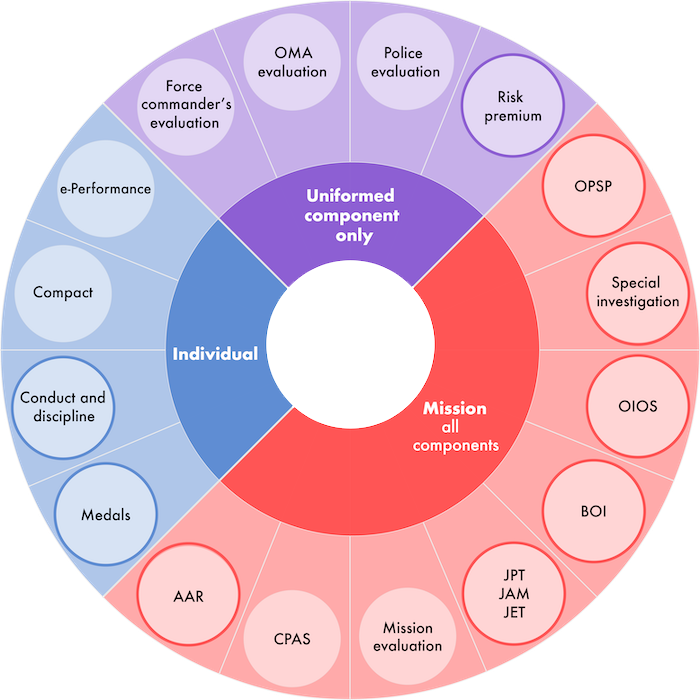
1. Force commander’s evaluation
2. OMA evaluation
3. Police evaluation
4. Risk premium
5. OPSP
6. Special investigation
7. OIOS
8. BOI
9. JPT/JAM/JET
10. Mission evaluation
11. CPAS
12. AAR
13. Medals
14. Conduct and discipline
15. Compact
16. e-Performance
Over the last two decades, UN peacekeeping operations have striven to protect civilians from physical violence. The protection of civilians (POC) is now based on a clear normative and policy framework, and its practical implementation relies on a number of innovative tools, tailored and multidimensional approaches, and the more proactive posture of peacekeepers. On a number of occasions, however, UN missions have failed to prevent or respond to threats despite being aware of the risk, receiving adequate warning of an attack, or being in the proximity when abuses were committed. Numerous reports and investigations into these incidents have highlighted shortcomings in performance and called for more accountability. Despite institutional ambitions, however, there is still limited accountability for the actors involved in protecting civilians.
To help address this challenge, IPI undertook a project to map how existing accountability mechanisms in the UN could be applied to peacekeeping missions with POC mandates. Through a combination of desk research and key informant interviews, IPI developed a set of tools to help guide the UN and its member states in building a robust, multi-actor, multilayer “system of accountability for POC.” These tools include:
- A policy paper analyzing the concept of accountability, identifying accountability mechanisms that exist and those that are needed, reviewing recent initiatives by the UN Secretariat and member states to strengthen accountability mechanisms for POC, and recommending steps that could be taken to strengthen these mechanisms further;
- An interactive graphic of the accountability mechanisms that can be or have been used to ensure accountability for the implementation of POC mandates by peacekeeping operations, with detailed fact sheets on each of these; and
- Case studies on how UN accountability tools have—or have not—been used in response to specific POC incidents in four different UN peacekeeping missions.
Collectively, these tools point to the need for a culture of active accountability for all actors, based on a shared willingness and commitment to assume responsibility and be answerable for the effective delivery of protection mandates. Toward this end, the policy paper offers the following recommendations:
- Working toward a more cohesive accountability structure by streamlining processes, improving coordination between accountability structures, broadening the scope of accountability tools to include all POC stakeholders, enhancing planning for POC, and tracking POC responses.
- Strengthening independent, dedicated, and transparent accountability tools by using more independent investigative teams, strengthening the role of the Office for Peacekeeping Strategic Partnership, providing dedicated resources for POC accountability, and striking a balance between transparency and politics.
- Enforcing consequences by following up on shortcomings in performance and considering POC in the force generation and selection processes, as well as going beyond punitive measures by developing incentives.