IPI’s research project on mechanisms to investigate attacks on healthcare aims to assist the Security Council, relevant UN organs, member states, and other stakeholders in operationalizing Resolution 2286 and the UN secretary-general’s recommendations for its implementation. The project focuses on recommendations regarding the use of international mechanisms to ensure that the “full, prompt, impartial and effective investigations” required by Resolution 2286 are carried out when parties to the conflict are unable or unwilling to do so themselves.
Through a combination of desk research, key informant interviews, and an expert meeting bringing together stakeholders in the implementation of Resolution 2286 and experts on international fact-finding and investigation into violations of international humanitarian law, the project developed a set of tools, available on this page. These include:
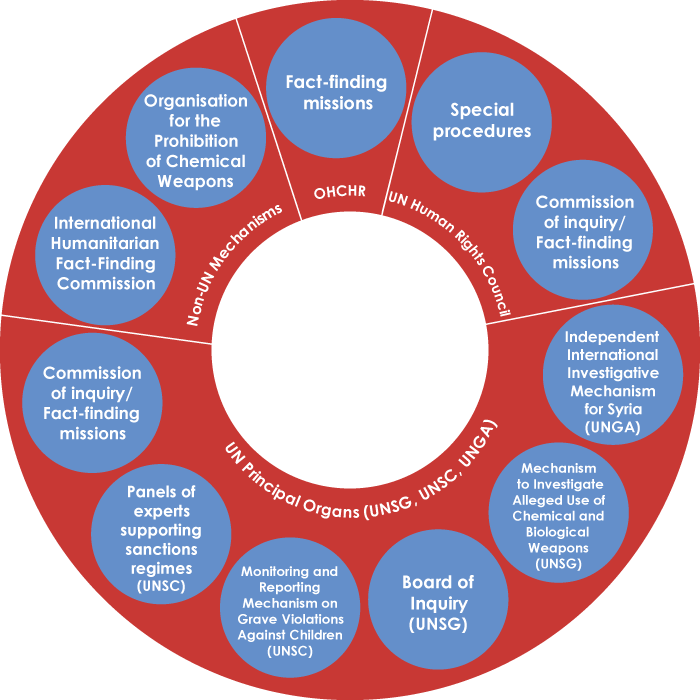
- A general mapping of mechanisms that can or have been used to investigate attacks on healthcare (facilities, personnel, patients, and means of transportation);
- An interactive graphic of the mechanisms evaluated in more detail for the project, with detailed fact sheets on each of these;
- A comprehensive list of investigations carried out by these mechanisms, highlighting those that looked into attacks on healthcare; and
- A research paper to supplement this broader set of tools, which should be read in conjunction with them.
Apart from introducing the topic and the research project and commenting on the project’s tools, the paper presents the project’s general findings on whether and how different mechanisms can be used to investigate attacks on healthcare. It also discusses their respective advantages and disadvantages and some of the inherent challenges in investigating violations of international law in situations of armed conflict. Finally, it submits a number of conclusions and a set of concrete recommendations to ensure existing mechanisms that could have a positive impact on the ground are used more systematically and effectively.
Author
Staff