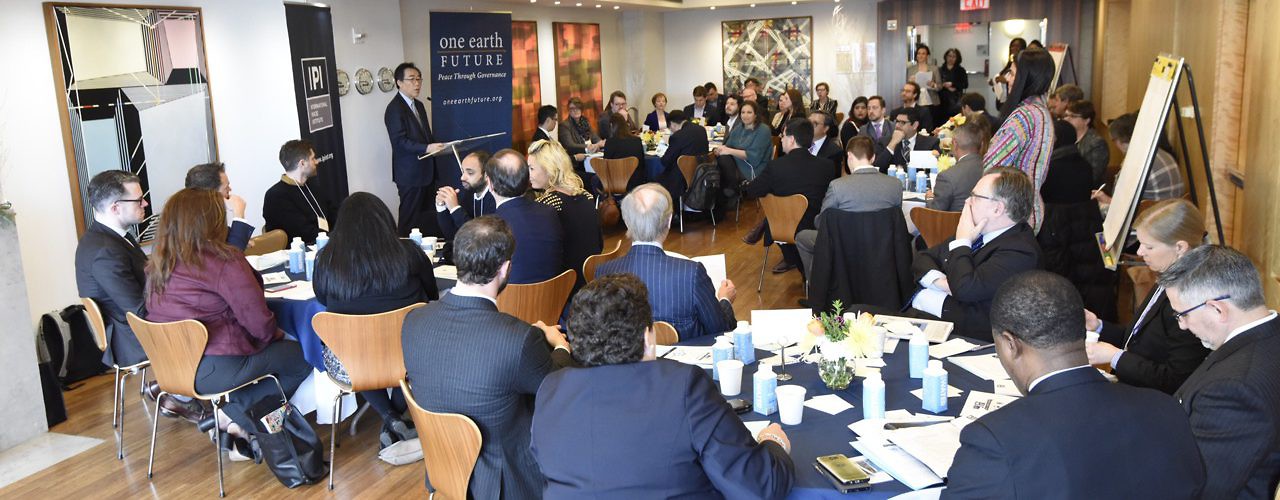
On December 4th, IPI, One Earth Future, UN Office for Partnerships, UN Peacebuilding Support Office, UN Global Compact, and the Permanent Mission of Republic of Korea launched a workshop series designed to catalyze engagement across public and private sectors and build new kinds of partnerships. While the private sector knows how to engage with topics such as economic growth and climate change, there is less understanding on how it can contribute to sustaining peace and the 2030 Agenda and how it can work together with the UN, member states and civil society.
The workshop was also focused on countries that need to scale up investments, particularly those that the private sector regard as too high-risk to engage.
The aim of creating this space was to address the main issue that has hindered effective cross-sectoral collaboration: an understanding gap between UN communities, civil society organizations, and private sector actors. Each of these communities interact with issues of peace and conflict in a different way, and without shared understanding about different starting points, attempts at partnerships may flounder. This workshop encouraged small-group discussion with country representatives, private sector actors, and civil society at the same table to develop shared understanding of each other and how collective work could be effective.
Table themes included: Fisheries/Food Security; Migration; Blended Finance; Measuring Peace; and Mobile and Digital Technology.
Some key points made by participants included:
- Business need to align their activities with the SDGs, not only because it is a noble cause, but because it makes financial sense;
- In order to make a “business case for peace” there is a need for a system thinking approach that addresses not only short-term needs but looks at the entire value chain;
- Knowledge-sharing and data are essential to create the needed frameworks for investors to engage in conflict and post conflict settings;
- Government buy-in is an indispensable requirement for businesses to invest in new projects that will have win-win outcomes;
- The private sector tends to overestimate risk and there is a need to do more evidence-based research to highlight that the benefits outweigh the risks; and
- The role of the UN is essential as a body that provides norms and standards as well as has a convening power that can build trust and credibility between different actors.
The private and public sectors have different definitions of peace and the workshop promoted a greater understanding of how to work collaboratively to address the SDGS and sustaining peace and how to develop “win-win” language for partnerships between the private sector and peace promoters.
The pilot session lasted approximately three hours and included about 60 participants drawn from member states, businesses, civil society organizations, and UN entities involved in sustainable development and peacebuilding. The discussions were conducted under the Chatham House Rule of non-attribution.
Related Coverage:
“OEF Announces Innovation in Partnerships Workshop,” Press Release, December 4, 2018