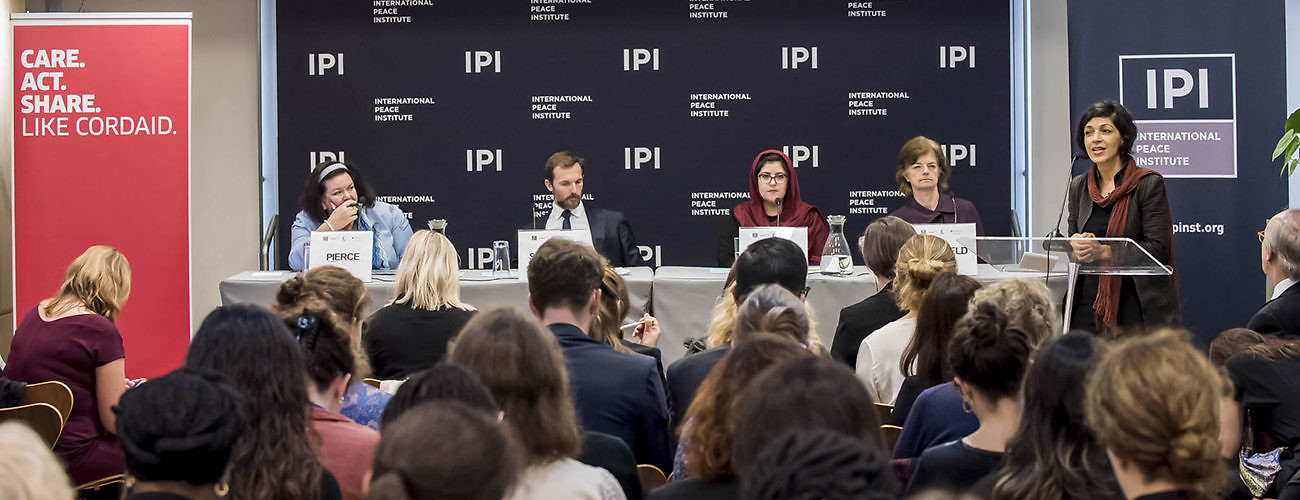
The international community’s role in supporting women as vital stakeholders in an inclusive and enduring peace in Afghanistan was the subject of an October 30th IPI policy forum cosponsored by Cordaid, the Georgetown Institute for Women, Peace and Security, and the NYU Center for Global Affairs.
Rina Amiri, Senior Fellow at the NYU center and longtime expert on peace and reconciliation in Afghanistan, said that while the world’s weariness with the ongoing Afghan war was speeding up people’s eagerness to come up with a way to end it, it was also resulting in concessions being made on earlier promises of inclusion. “Women’s rights and inclusion has moved from an absolute priority of the international community to something that is relegated just to inter-Afghan talks,” she said.
In light of this, she asked, “What are the arguments that we need to make that we’re not making, how can we move from lip service to genuine commitment, what are the ways that we should be thinking about inclusion and process design?”
IPI Senior Fellow Sarah Taylor spoke of a disturbing discordance between the pledges of UN member states to the women, peace and security agenda that she heard voiced in the Security Council debate on the subject the day before and the reality that women are still being kept from positions of power and influence 19 years after the passage of the landmark resolution 1325. She alluded to the example of the work done in Sudan by women “putting their bodies on the line, breaking curfews, braving tear gas yet still excluded from the discussions that determine the future of their communities.”
Storai Tapesh, Deputy Executive Director, Afghan Women’s Network, said that recent peace negotiations between the Taliban and the United States in the Qatari capital Doha allowed for more women’s participation than in past talks but still did not attract the necessary support from the international community. “We saw the added value of women during the recent dialogues in Doha,” she said. “It was us, the women of Afghanistan, who were putting important issues on the table. As opposed to the men, we were not negotiating out of a position of self-interest but pushing the real issues such as human rights, the red lines of the constitution and the need for an immediate ceasefire.”
Though those talks have now stalled, Ms. Tapesh said the women of Afghanistan are still “very much committed” to them and want to see them resumed and “facilitated” by the international community. Clarifying the kind of support they needed, she said, “Afghan women do not want you to fight our battles; we need support for our voices and space to advocate for peace.”
Testifying to the importance of women’s inclusion to the sustainability of peace processes, Karen Pierce, Permanent Representative of the United Kingdom to the United Nations, said, “You cannot actually build a truly prosperous society that enables any country to realize its full potential if you exclude some 50% of the population from the economic and legal life of the country, never mind the social. More than half of all peace processes collapse within five years if they don’t have sustainable provisions, and those sustainable provisions have been shown in well-documented evidence to include gender and women’s provisions.”
Ambassador Pierce was asked by the discussion moderator, Jake Sherman, director of IPI’s Brian Urquhart Center for Peace Operations, about how to balance the push for women’s rights with the overall push for a peace accord without one jeopardizing the other. “You must have some very robust clauses about human rights and women’s rights, but I don’t know if in a negotiation with an informal organization such as the Taliban, it is good to go in loudly with your red lines,” she said. Instead, she explained, “the point at which you ask for the things you really need is at the end when peace is in sight.” Signaling the critical nature of this sequencing, she warned, “When we sacrifice the long term goal for short term expediency, we end up regretting that quickly and find ourselves back at the table negotiating peace again.”
Ms. Pierce acknowledged that it was particularly difficult to introduce the subject of women’s rights into conversations with the Taliban, a group notorious for its overt sexism and violence against women. “But the fact that is a difficult argument isn’t an argument for not making it,” she said. She added that those who counsel taking up the subject only “at the pace that the Taliban want” are ignoring evidence of women’s rights having been brought into the process successfully with tact, good timing and persistence. “You do it incrementally, you do it gradually, but above all, you do it steadily, don’t go backward.”
Mahbouba Seraj, a member of the Afghan Women’s Network, urged the international community to adopt a principled position on Afghanistan without regard to pleasing one side or the other. “Do not worry about the Taliban or Trump, but take a stance because if you don’t do that and stay on the basis of being wishy washy with the Taliban, then they are going to take advantage of that.”
Teresa Whitfield, Director, Policy and Mediation Division, UN Department of Political and Peacebuilding Affairs, said that actions to include women in peace processes had to go beyond the numbers. “We need to normalize the process that women have substantive contributions in peace processes and not just that there are two women at the table,” she said. She asserted that obtaining respect for Afghan women’s rights would require a “creative” approach, given the nature of the Taliban. “The Taliban doesn’t include women in leadership so we cannot recruit and include them through their political or military power,” she said. Among the alternatives from her office’s experience that she suggested were advisory boards, gender subcommittees, women lawyers, broad consultations with civil society, online platforms, and social media information sharing.
In conclusion, Ms. Whitfield stressed, “The absolutely fundamental need for those of us who represent the international community and are on the outside of conflicts is to put in the legwork, the analysis, the research, the knowledge, and always focus on harnessing international forces. The demand for Afghan women’s rights comes from Afghan women, and that’s what needs to be represented in some shape or form at the table in the peace process.”