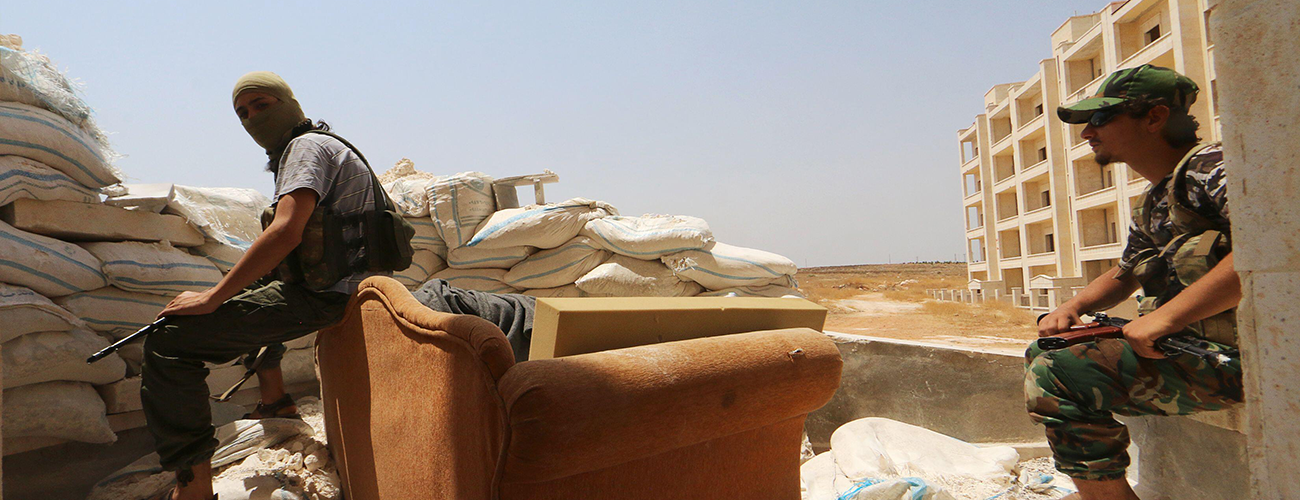
Al-Nusra Front fighters rest with their weapons behind sandbags in the Sheikh Maksoud neighborhood of Aleppo, Syria on August 3, 2015. (Reuters/Abdalrhman Ismail)
While only a small percentage of men become involved in violent extremism, the majority of violent extremists are men. Across the ideological spectrum, violent extremist and terrorist groups exploit male sentiments of emasculation and loss of power and appeal to ideas of manhood in their recruitment efforts. Yet policymakers rarely focus on gender to help them understand why some men engage in violence and others do not or what role peaceful notions of masculinity play in preventing radicalization and terrorism. Similarly, male-dominated counterterrorism institutions rarely pose the question of how masculinities shape these institutions and their approaches to counterterrorism and countering violent extremism (CVE).
This report discusses masculinities—the socially constructed ideas of what it means to be a man—as they are constructed and used by violent extremist groups, as they exist in and interact with society, and as they interplay with the state. It draws on examples pertaining to both “Islamist” and extreme right-wing terrorism, considering differences not just between but also within these ideologies.
The report argues that while current efforts to “mainstream gender” in counterterrorism and CVE do not focus on masculinities, a masculinities-focused approach must avoid repeating the shortcomings of existing counterterrorism and CVE approaches aimed at women; be grounded in a robust human rights framework to avoid perpetuating gendered harms; be based on an understanding of the links between extremist violence and gender inequality at the societal level; and recognize and address the harmful role masculinities play within counterterrorism and CVE institutions themselves. It concludes by recommending that state, multilateral, and civil society actors engaged in counterterrorism and CVE:
- Conduct more policy-oriented research and analysis on the link between masculinities and violent extremism;
- Integrate a gender perspective—including a focus on masculinities—across all counterterrorism and CVE policy and programming;
- Monitor and evaluate the gendered impact of counterterrorism and CVE interventions using a robust human rights framework; and
- Address the harmful role masculinities play within counterterrorism and CVE institutions.