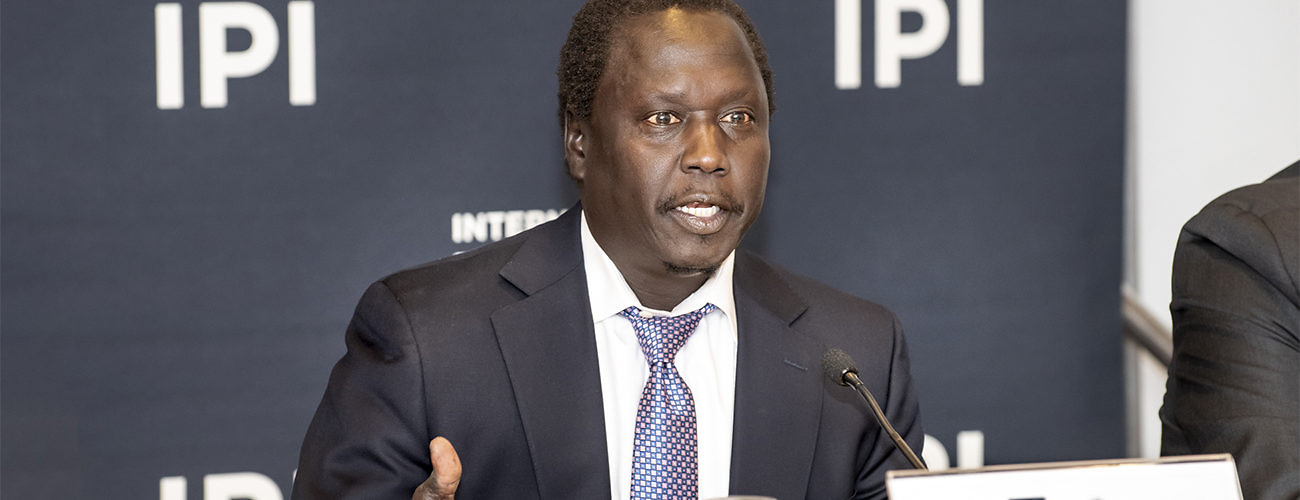
A broad-based mediation plan in South Sudan to try to forge peace after violence devastated the country between 2013 and 2015 unraveled in a year, plunging the country back into conflict. On April 30th, IPI and the Permanent Mission of Finland to the United Nations held a policy forum to discuss the subject and launch a new report A Poisoned Well: Lessons in Mediation from South Sudan’s Troubled Peace Process that assesses the strengths and weaknesses of the mediation architecture and the role played by the individuals and institutions that tried with little success to put it in place.
Reviewing the lapsed process, Jouni Laaksonen, the Deputy Permanent Representative of Finland, said his country put a high premium on making it more inclusive. “The inclusive approach to peacebuilding is necessary for the achievement of permanent results, and sustaining peace requires the involvement of all actors, from different parts of society,” he said.
The report focused on the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD), the eight-nation bloc of African countries that led the mediation effort, along with other national and international actors. This network of regional interests, while welcome in principle, frequently broke down in practice, said the author of the report, Zach Vertin, Visiting Lecturer at Princeton’s Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs.
“Mediators were not sufficiently empowered by their own bosses,” he said, “so when the process stalled, which was often, it would require the heads of state from the entire region to convene. This ate up huge amounts of time and resources and slowed the process at critical moments. Now this sustained commitment from high-level actors was important in a theoretical sense but at the same time had effectively undercut the mediators in the eyes of the parties.”
Two other critical roadblocks, Mr. Vertin said, were a failure to achieve consensus on the scope and nature of the problem and an absence of political will among the various sides in the struggle. He explained, “The parties themselves and South Sudan’s warring combatants not only lacked the will to make peace, there were often a number of them very hostile to the very idea of a negotiated settlement.” He said it raised the question of “how do outside actors compel a mediated resolution of a conflict between two parties bent on war?”
One specific failure he identified was not imposing an arms embargo on the fighters, in effect fueling more violence at the same time that peacemakers were trying to quell it.
Mr. Vertin spent the years 2013 to 2016 in South Sudan and Sudan, both as a US diplomat and an adviser to IGAD, and he said the experience left him pondering a larger question. “Is there a formula that couples regional players and their comparative advantage with other mediation expertise?”
Jok Madut Jok, Executive Director of The Sudd Institute and a resident of South Sudan, wondered if putting so much authority in the hands of outsiders and experts didn’t end up producing a “peace agreement, but no peace and stability in the real lives of people.” He also questioned how effectively they prioritized the needs of the local people over their own national ambitions.
He asked, “How can regional leaders who are mediating the situation in South Sudan be prevented from looking at South Sudan purely from the point of view of their own view, political interests? …How is it going to be possible to prevent them from only looking at the conflict from the point of view of how it affects them, and not necessarily from the perspective of what the South Sudanese need that peace agreement to look like?”
He added that he was skeptical of the value of global engagement in general in South Sudan because too often the South Sudanese exploited international assistance and took no action on their own to resolve conflict, assured that “the outside world would always bail them out.”
François Grignon, the Department of Peacekeeping Operations team leader for South Sudan since 2011, said the mediation process there had exposed the weakness of too much reliance on “textbook” remedies rather than ones developed to suit the realities of the country. “Unless we succeed to adapt our instruments to have leverage on the actors of the violence,” he said, “we will continue to struggle with mediation or with the peace process, which will miss the point, because it follows textbooks, or because it follows templates, which…may not be necessarily relevant and efficient and effective in addressing the specifics of this situation.”
“So,” he said, “maybe there’s another way to do it–civil engagement, civil activity. South Sudanese are so divided that they are afraid of each other. That if they are ever going to have a say in who rules them, then rebuilding those ethnic relations across the board is going to be the only way they can actually speak about removing a president and installing a transitional government up to the time when you will have elections.”
IPI Research Fellow Sarah Taylor was the moderator.